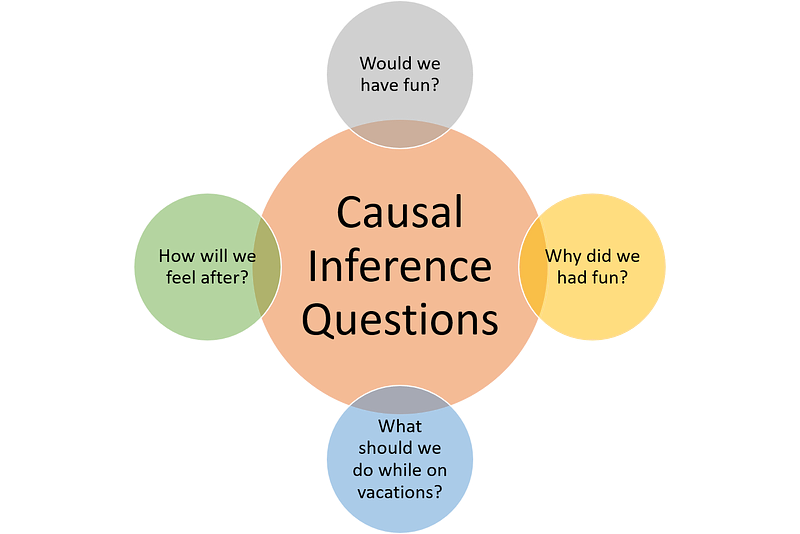
Causal Inference is the process of determining if a change in one variable causes a change in another...
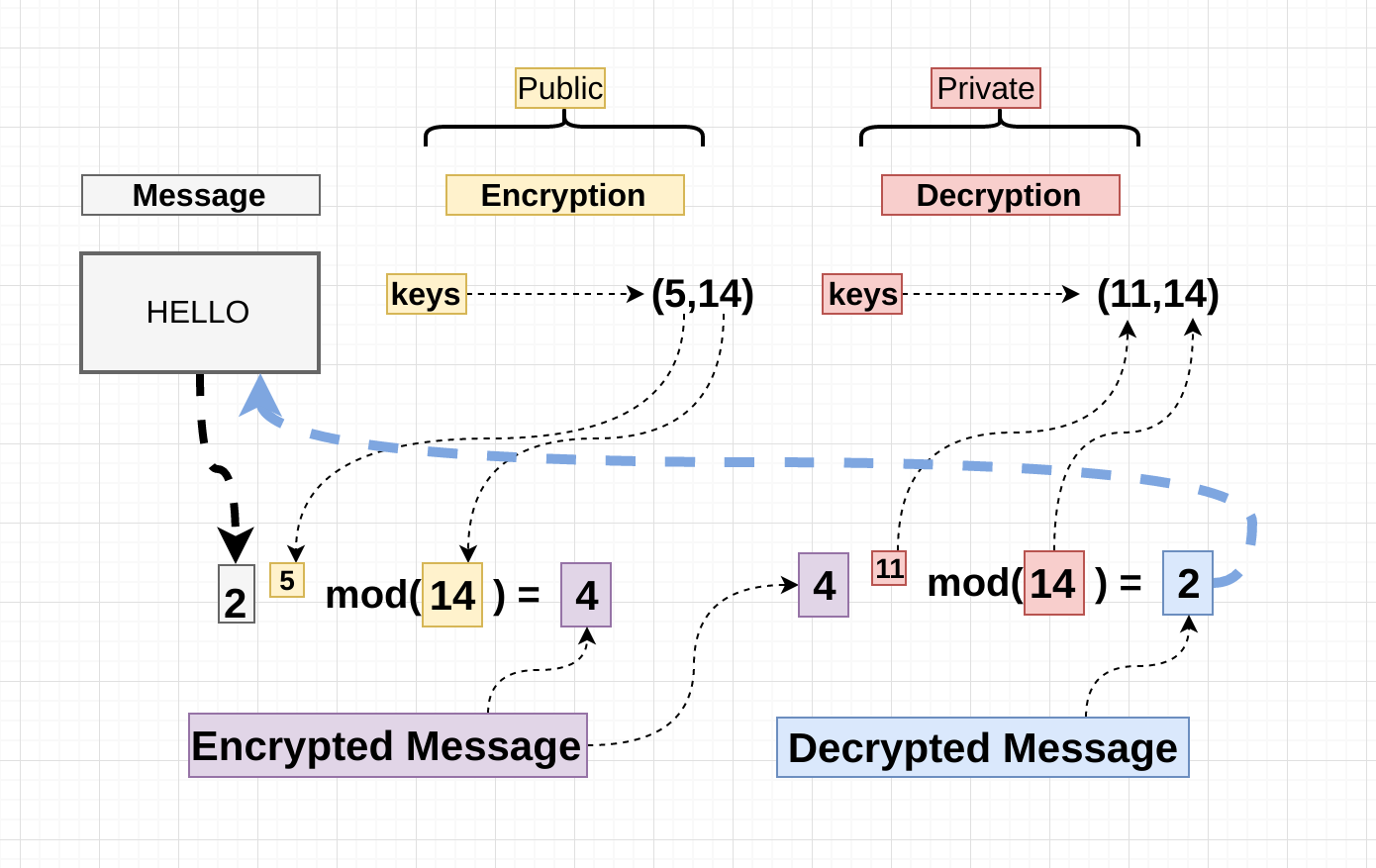
RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) is a public-key cryptosystem that enables secure communication over insecure channels. Named after its inventors Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman,...
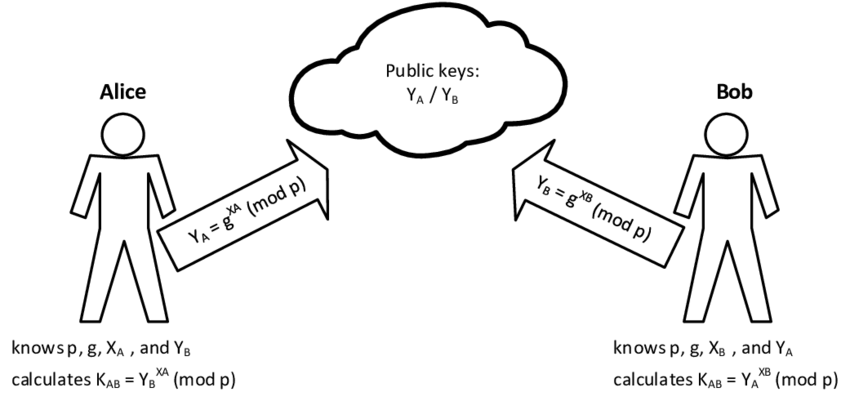
The Diffie-Hellman (DH) Key Exchange is a method for two parties to establish a shared secret key over an insecure communication channel. Proposed by Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman in 1976...
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and programs from digital attacks. These cyberattacks are usually aimed at accessing, changing, or destroying sensitive information; extorting money from users; or interrupting normal business processes....
In today's interconnected world, cybersecurity is not just about protecting data—it is about safeguarding our digital lives. This comprehensive guide explores nine critical cybersecurity....
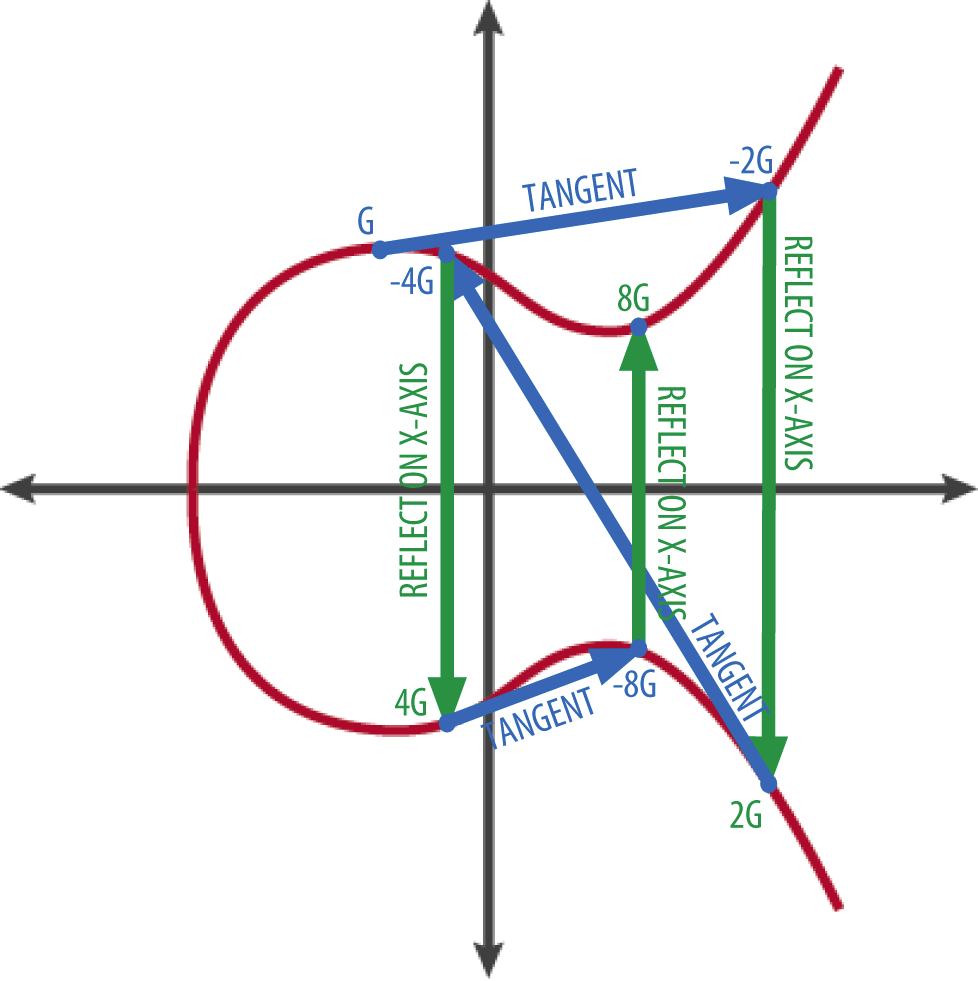
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is a form of public-key cryptography that uses the algebraic structure of elliptic curves over finite fields. Proposed independently by Neal Koblitz and Victor Miller in 1985....